SOFTWARE TESTING 1st Chapter:
Q 1. What is an Agile Process ? State its
principles.
==>
ð
Explanation:-
1) Agile
software development is not only a process but it referred as philosophy.
2)
The agile software development focuses on the rapid development of the software
product by
considering the current market requirements and time limits.
3)
Agile development focuses on face to face or interactive processes than
documentation.
4)
It helps
in quickly transferring the ideas.
5)
Agile software development saves man power, cost, documentation and most importantly time.
6)
It is recent
approach for Project Management.
7)
Agile process model uses the cocept of Extreme Programming.
8)
Agile focuses
on modularity, iterative, time bound, parsimony, adaptive, incremental
convergent, collaborative approach.
9)
Today’s market is rapidly changing and
unpredictable too. Root of agile software development is in the reality of
today’s markets.
10)
If we compare
waterfall model with agile software development, we find agile software
development is very much useful and practically applicable.
11)
It does not believe in more and more
documentation because it makes difficult to find out the required information.
12)
It supports teams
to work together with management for supporting technical decision making.
13)
This method focuses mainly on the coding because directly deliverable to
the users.
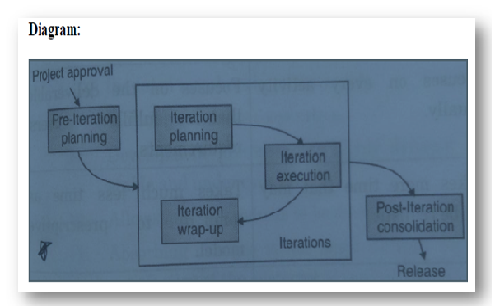
Q 2. Explain about the incremental model.
==>
Diagram:-
1) Incremental model is also called as iterative enhancement model.
2) In this model the software is built in an incremental fashion.
3) Fig shows the
project is divided into small subsets called as increments and are implemented by
individually.
4)
In
this model the product is designed, implemented, integrated and tested as a
series of incremental builds.
5)
The incremental model combines elements of the linear sequential model with the iterative
philosophy of prototyping,
6) Each
linear sequence produces deliverable increments of the software.
7)
The
incremental model is iterative in nature. When an incremental model is used,
the first increments are often a “core product”.
8) Thai
is basic requirements are addressed, but many supplementary features remain
undelivered.
9) Incremental
development is useful when staffing is unavailable for a complete implementation
by the business deadline that has been established for the project.
10) Each build consist of code pieces from
various modules interacting to provide a specific functional capability.
·
Example:
Word processing
software developed using the incremental paradigm, might deliver basic file management
editing and document production in the first increment, more sophisticated editing and document production capabilities in
second increment, Spelling and grammar checking in
third increment and advanced page layout
capability in fourth increment and at the end the software get’s ready to use.
Q 3. Explain RAD model and state the drawbacks of it.
Diagram:-
Explanation:-
1) RAD
is modern software process that focus on a short development cycle.
2)
The RAD is “High speed” adaption then of
waterfall model in which rapid development is achieved.
3)
As compared to waterfall model team size
of RAD model is large to function with proper coordination.
4)
If requirement are well understood
and project scope is considered, the RAD process is create a “Fully
functionally system” within a very short period of time (normaly 60 to 90
days).
Drabacks:
1.
RAD
model needs enough human resources to create the required number of RAD teams.
2.
If
developers and customers are not committed to the rapid model, the RAD project
fails.
3.
Rapid-fire
activities need to be completed in very short or small time frame. Time is the major constraint in RAD.
4.
RAD
has to be modularized in a proper way otherwise creates a lots of confusions
and problems.
5.
In
case of high performance requirement, RAD cannot be ideal model.
6.
Still
if RAD model has to be used then it can be done by making tune between
interface and system components.
Q
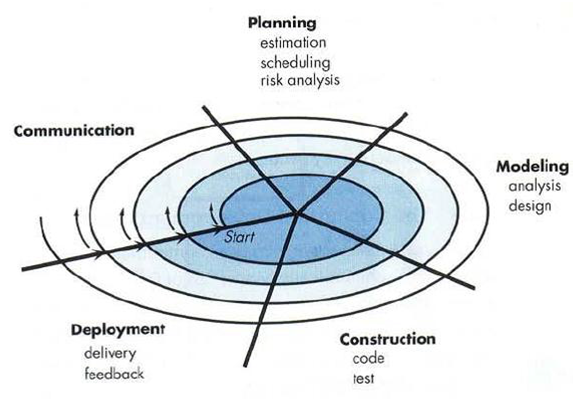
4.
Spiral model is a realistic approach to the development of Large-Scale systems and software. Justify and
explain the model ?
==>
Diagram:-
1) From
the figure given above, a spiral model is divided into a set of framework activities defined by the software engineering
team.
2) As
this evolutionary process begins, the software team performs activities in a
clockwise direction, beginning at the center.
3) Spiral
model combines development activities with risk management to minimize and
control the risk impact.
4) It
also provides scope for RAD for increasingly complete software.
5) Cost
& schedule are adjusted based on feedback derived from the customer after
delivery.
6) In
addition, the project manager adjusts the planned number of iterations required
to complete the software.
7) This
may be a realistic approach for large scale software development.
8) As
the process progresses both users and developers better understand the system.
Advantages:
1. One is a cyclic approach for
incrementally growing a system‘s degree of definition and implementation while
decreasing its degree of risk.
2. The
set of anchor point milestones for ensuring stakeholder commitment to obtain
feasible and mutually satisfactory system solutions.
Limitations:
1. The system demands risks
identification and monitoring to prevent hurdles.
2. System
can get into infinite iterations.
Q 5. What are the characteristis of the software ?
-->
1.
Functionality:
It refers to the
degree of performance of the software against its intended purpose.
2. Reliability:
It
refers to the ability of the software to provide desired functionality under
the given conditions.
3. Usability:
It refers to the
extent to which the software can be used with ease and simple.
4.
Maintainability:
Software must
evolve to meet changing needs.
5.
Dependability:
Software must be
trustworthy.
6. Efficiency:
Software should
not make wasteful of system resources.
7.
Acceptability:
Software must
accepted by the users for which it was designed.
8. Portability:
It
refers to the ease with which software developers can transfer software from
one platform to another, without changes.
9. Integrity:
It refers to the
degree to which unauthorized access to the software can be prevented.
10. Robustness:
It
refers to the degree to which the software can keep on functioning in spite of
being provide with invalid data.
Q
6 .Explain extreme programming concept ?
==>Diagram:
1) EXtreme Programming (XP) was conceived and developed
to address the specific needs of software development by small teams in the
face of changing requirements.
2) Extreme Programming is one
of the Agile software development methodologies.
3) It provides values and
principles to guide the team behavior. The team is expected to self-organize.
4) Extreme Programming provides
specific core practices where −
• Each practice is simple
and self-complete.
• Combination of practices
produces more complex and emergent behavior
*Why is it
called “Extreme"?
Extreme Programming takes the effective principles and practices to
extreme levels.
1. Code reviews are effective
as the code is reviewed all the time.
2. Testing is effective as
there is continuous regression and testing.
3. Design is effective as
everybody needs to do refactoring daily.
4. Integration testing is
important as integrate and test several times a day.
5. Short iterations are
effective as the planning game for release planning and iteration planning.
Q 7. State & explain XP
practice principles
è Extreme Programming is based on 9 principles:
1.
The planning process
2.
Small releases
3.
Metaphor
4.
Simple design
5.
Testing
6.
Refactoring
7.
Pair programming
8.
Colective ownership
9.
Continuous integration
The
Planning Process - The desired features of the software, which are
communicated by the customer, are combined with cost estimates provided by the
programmers to determine what the most important factors of the software are.
This stage is sometimes called the Planning Game.
Small
Releases -
The software is developed in small stages that are updated frequently,
typically every two weeks.
Metaphor
-
All members on an XP team use common names and descriptions to guide
development and communicate on common terms.
Simple
Design -
The software should include only the code that is necessary to achieve the
desired results communicated by the customer at each stage in the process. The
emphasis is not on building for future versions of the product.
Testing
-
Testing is done consistently throughout the process. Programmers design the
tests first and then write the software to fulfill the requirements of the
test. The customer also provides acceptance tests at each stage to ensure the
desired results are achieved.
Refactoring
-
XP programmers improve the design of the software through every stage of
development instead of waiting until the end of the development and going back
to correct flaws.
Pair
Programming -
All code is written by a pair of programmers working at the same machine.
Collective
Ownership -
Every line of code belongs to every programmer working on the project, so there
are no issues of proprietary authorship to slow the project down. Code is
changed when it needs to be changed without delay.
Continuous
Integration -
The XP team integrates and builds the software system multiple times per day to
keep all the programmers at the same stage of the development process at once.
Q 8. What do you mean
by evolutionary process flow ? Explain any one evolutionary process model?
==> Diagram:
1. The evolution model
divides the development cycle into smaller, "Incremental Waterfall
Model" in which users are able to get access to the product at the end of
each cycle.
2. The users provide
feedback on the product for planning stage of the next cycle and the
development team responds, often by changing the product,plans or process.
3. These incremental cycles
are typically two or four weeks in duration and continue until the product is
shipped.
1) These models are more
suited to object oriented systems.
2) They are iterative in
Process.
3) They enable the software
developer to develop increasingly more Complex versions of the software.
4) Like all Complex systems,
software involve over period of the time and hence evolutionary models are more
suited to software development.
5) Requirements gets changed
while the software is under development.
·
Advantages of
Evolutionary Model:-
1) Error reduction: As the version is
tested with customer which reduces the error throughlly.
2) User satisfaction: User gets satisfied and
he gets the full chance of experimenting partially developed system.
3) Business benefit: Successful use of this
model can benefit not only business result but marketing and the internal
operations as well.
4) High quality: As you should get
satisfied with every version, it produces the high quality product.
5) Low risk: There is significant
reduction of risk as a versions is implemented. This risk may be associated
with
6) missing schedule deadline
7) wrong feature sets
8) poor quality
9) Reduction Cost: Some design issues are
cheaper to resolve through experimentation than through analysis. It reduces
cost by providing structured and disciplined avenue for experimentation.
·
Disadvantages of
Evolutionary Model:-
1) Several version release: Developer has to make
table version which increases their Efforts.
2) Dividing software: It is difficult to
"divide the software and the problems in several versions that would be
acceptable to the customer which can be implemented and delivered
incrementally.
3) Uncertain nature of
customer needs:
A confused user has uncertainty over his requirements, so giving him several
version may change his requirement Rapidly.
4) Time And Cost:As this model reduces
"Time And Cost" but requirement is not gathered correctly. It will
subsequently time, cost and efforts.
5) Confusion by several
version:
An user might get "confused by several versions of the software. It will
affect on the final product.






No comments:
Post a Comment